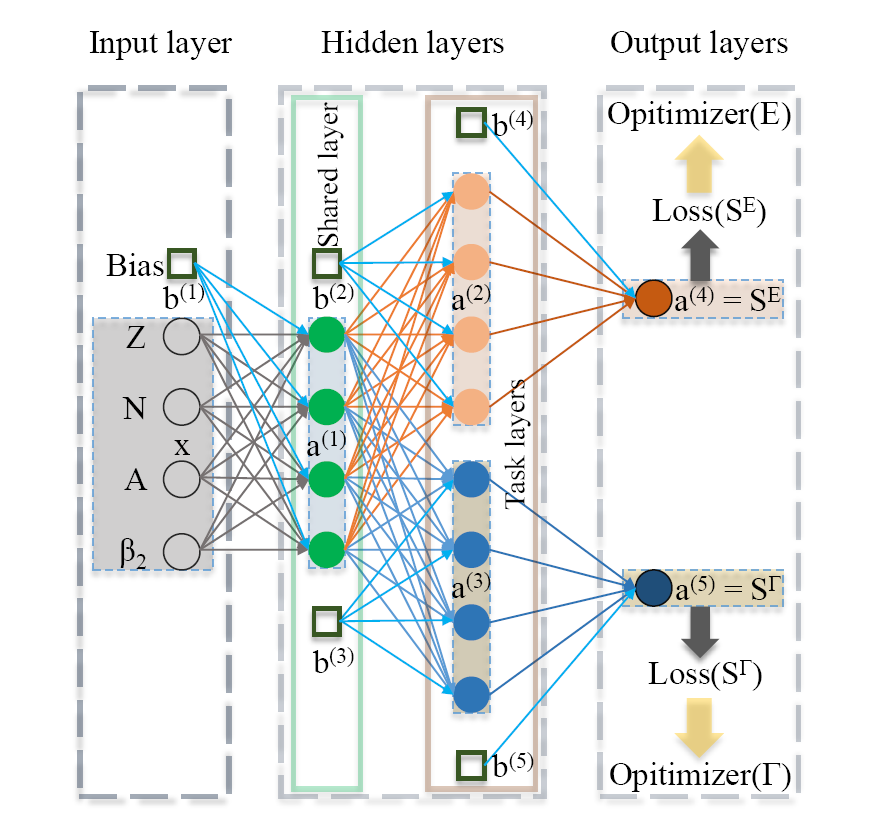
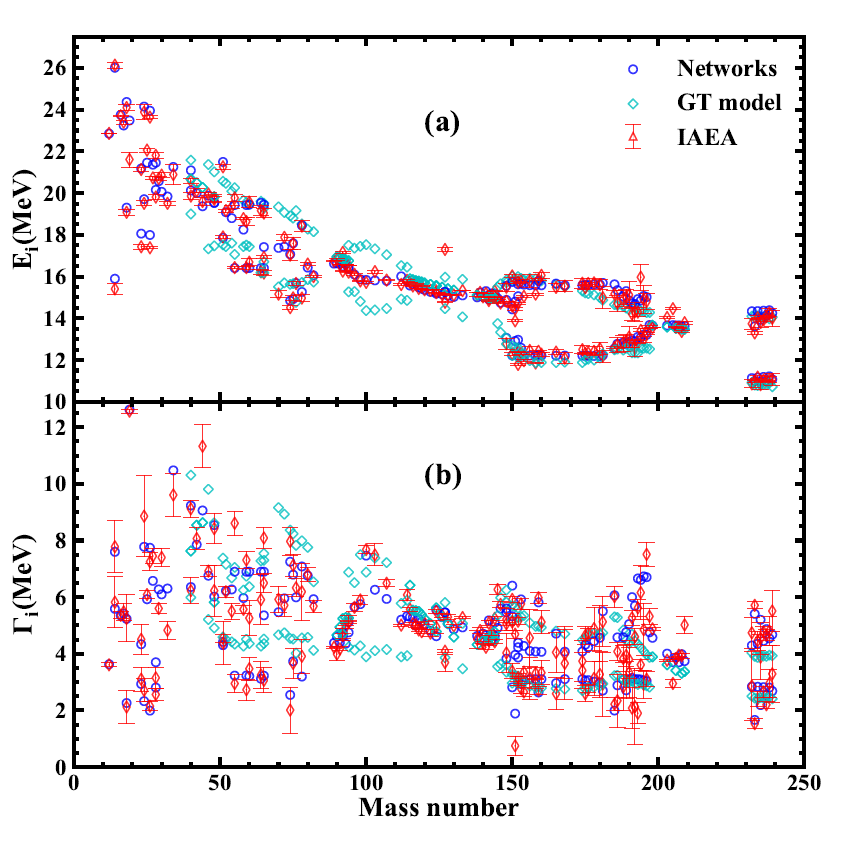
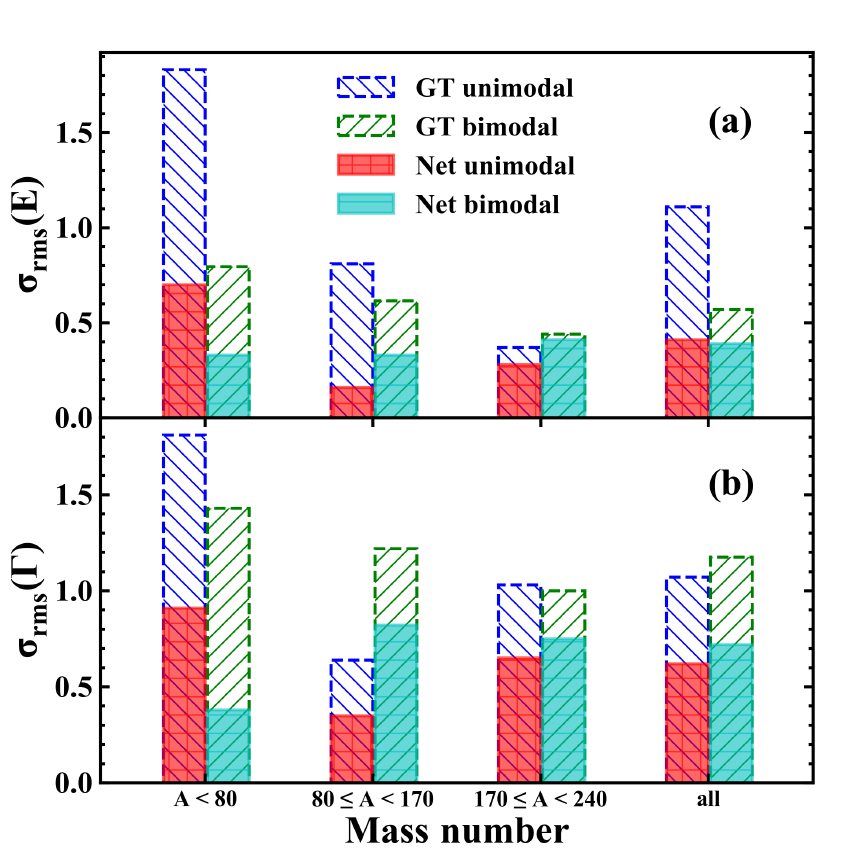
巨偶极共振(GDR)是原子核中最基本的集体激发模式之一。不同的核数据库对GDR关键参数的评估作出不断的努力。我们引入了多任务学习(MTL)方法来学习和再现已评估的GDR关键参数的实验数据,包括GDR的能量和宽度。与RIPL-3数据库中的GDR理论参数相比,MTL方法的精度对129个核的实验数据几乎提高了一倍。这主要归功于分类神经网络对单峰核和双峰核的正确分类。基于神经网络方法的良好表现,对β-稳定线附近的79个没有实验数据的核进行了外推,为今后的实验和数据评估提供了重要参考。MTL方法在本工作中的成功应用进一步证明了多任务神经网络在核物理领域研究多输出物理问题的可行性。
相关论文发表在 Physics Letters B 815, 136147 (2021)
文章标题: The description of giant dipole resonance key parameters with multitask neural networks
文章链接: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2021.136147
摘要:
Giant dipole resonance (GDR) is one of the fundamental collective excitation modes in nucleus. Continu-ous efforts have been made to the evaluation of GDR key parameters in different nuclear data libraries. We introduced multitask learning (MTL) approach to learn and reproduce the evaluated experimental data of GDR key parameters, including both GDR energies and widths. Compared to the theoretical GDR parameters in RIPL-3 library, the accuracies of MTL approach are almost doubled for 129 nuclei with ex-perimental data. The significant improvement is largely due to the right classification of unimodal nuclei and bimodal nuclei by the classification neural network. Based on the good performance of the neural network approach, an extrapolation to 79 nuclei around the β-stability line without experimental data is made, which provides an important reference to future experiments and data evaluations. The successful application of MTL approach in this work further proofs the feasibility of studying multi-output physical problems with multitask neural network in nuclear physics domain.